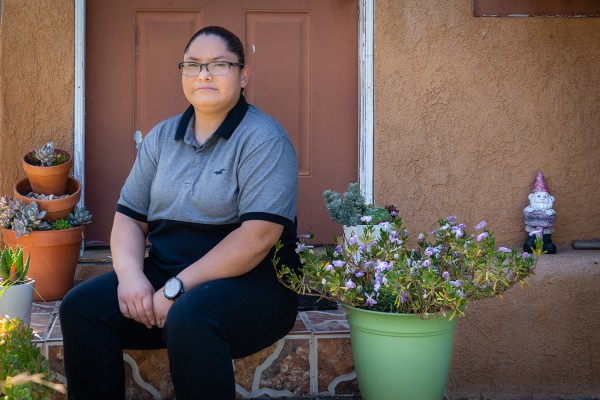
Carmen Quintero trabaja como supervisora en un centro de distribución de máscaras N95. El 23 de marzo contrajo síntomas similares a COVID, pero no pudo hacerse una prueba. Ella debe $ 1,840 por otra atención que recibió cuando “sospechaba de COVID”. Foto: Heidi de Marco / KHN.
By Sarah Varney
Kaiser Health News
Carmen Quintero works an early shift as a supervisor at a 3M distribution warehouse that ships N95 masks to a nation under siege from the coronavirus. On March 23, she had developed a severe cough, and her voice, usually quick and enthusiastic, was barely a whisper.
A human resources staff member told Quintero she needed to go home.
“They told me I couldn’t come back until I was tested,” said Quintero, who was also told that she would need to document that she didn’t have the virus.
Her primary care doctor directed her to the nearest emergency room for testing because the practice had no coronavirus tests.
Send Us Your Medical Bill
Bill of the Month logo
Do you have an exorbitant or baffling medical bill? Join the KHN and NPR ‘Bill of the Month’ Club and tell us about your experience. We’ll feature a new one each month.
The Corona Regional Medical Center is just around the corner from her house in Corona, California, and there a nurse tested her breathing and gave her a chest X-ray. But the hospital didn’t have any tests either, and the nurse told her to go to Riverside County’s public health department. There, a public health worker gave her an 800 number to call to schedule a test. The earliest the county could test her was April 7, more than two weeks later.
At the hospital, Quintero got a doctor’s note saying she should stay home from work for a week, and she was told to behave as if she had COVID-19, isolating herself from vulnerable household members. That was difficult — Quintero lives with her grandmother and her girlfriend’s parents — but she managed. No one else in her home got sick, and by the time April 7 came, she felt better and decided not to get the coronavirus test.
Then the bill came.
The Patient: Carmen Quintero, 35, a supervisor at a 3M distribution warehouse who lives in Corona, California. She has an Anthem Blue Cross health insurance plan through her job with a $3,500 annual deductible.
Total Bill: Corona Regional Medical Center billed Quintero $1,010, and Corona Regional Emergency Medical Associates billed an additional $830 for physician services. She also paid $50 at Walgreens to fill a prescription for an inhaler.
Service Provider: Corona Regional Medical Center, a for-profit hospital owned by Universal Health Services, a company based in King of Prussia, Pennsylvania, which is one of the largest health care management companies in the nation. The hospital contracts with Corona Regional Emergency Medical Associates, part of Emergent Medical Associates.
Medical Service: Quintero was evaluated in the emergency room for symptoms consistent with COVID-19: a wracking cough and difficulty breathing. She had a chest X-ray and a breathing treatment and was prescribed an inhaler.
Some insurance companies are voluntarily reducing copayments for COVID-related emergency room visits. Quintero said her insurer, Anthem Blue Cross, would not reduce her bill. Anthem would not discuss the case until Quintero signed its own privacy waiver; it would not accept a signed standard waiver KHN uses. The hospital would not discuss the bill with a reporter unless Quintero could also be on the phone, something that has yet to be arranged around Quintero’s workday, which begins at 4 a.m. and ends at 3:30 p.m.
Three states have gone further than Congress to waive cost sharing for testing and diagnosis of pneumonia and influenza, given these illnesses are often mistaken for COVID-19. California is not one of them, and because Quintero’s employer is self-insured — the company pays for health services directly from its own funds — it is exempt from state directives anyway. The U.S. Department of Labor regulates all self-funded insurance plans. In 2019, nearly 2 in 3 covered workers were in these types of plans.
Resolution: As lockdown restrictions ease and coronavirus cases rise around the country, public health officials say quickly isolating sick people before the virus spreads through families is essential.
But isolation efforts have gotten little attention in the U.S. Nearly all local health departments, including Riverside County, where Quintero lives, now have these programs, according to the National Association of County and City Health Officials. Many were designed to shelter people experiencing homelessness but can be used to isolate others.
Raymond Niaura, interim chairman of the Department of Epidemiology at New York University, said these programs are used inconsistently and have been poorly promoted to the public.
“No one has done this before and a lot of what’s happening is that people are making it up as they go along,” said Niaura. “We’ve just never been in a circumstance like this.”
Quintero still worries about bringing the virus home to her family and fears being in the same room with her grandmother. Quintero returns from work every day now, puts her clothes in a separate hamper and diligently washes her hands before she interacts with anyone.
The bills have been another constant worry. Quintero called the hospital and her insurance company and complained that she should not have to pay since she was seeking a test on her doctor’s orders. Neither budged, and the bills labeled “payment reminders” soon became “final notices.” She reluctantly agreed to pay $100 a month toward her balance — $50 to the hospital and $50 to the doctors.
“None of them wanted to work with me,” Quintero said. “I just have to give the first payment on each bill so they wouldn’t send me to collections.”
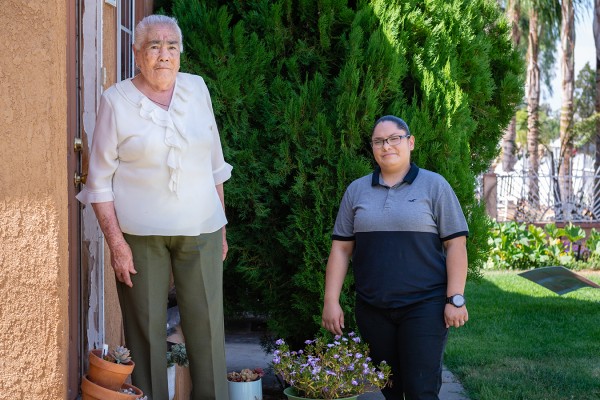

Carmen Quintero (right) still tries to keep a safe distance from her grandmother, Teresa Carapia, and two other family members over 65. Quintero says she worried about them as she tried to self-isolate with COVID-like symptoms (Heidi de Marco/KHN).
Some insurance companies are voluntarily reducing copayments for COVID-related emergency room visits. Quintero said her insurer, Anthem Blue Cross, would not reduce her bill. Anthem would not discuss the case until Quintero signed its own privacy waiver; it would not accept a signed standard waiver KHN uses. The hospital would not discuss the bill with a reporter unless Quintero could also be on the phone, something that has yet to be arranged around Quintero’s workday, which begins at 4 a.m. and ends at 3:30 p.m.
Three states have gone further than Congress to waive cost sharing for testing and diagnosis of pneumonia and influenza, given these illnesses are often mistaken for COVID-19. California is not one of them, and because Quintero’s employer is self-insured — the company pays for health services directly from its own funds — it is exempt from state directives anyway. The U.S. Department of Labor regulates all self-funded insurance plans. In 2019, nearly 2 in 3 covered workers were in these types of plans.
Resolution: As lockdown restrictions ease and coronavirus cases rise around the country, public health officials say quickly isolating sick people before the virus spreads through families is essential.
But isolation efforts have gotten little attention in the U.S. Nearly all local health departments, including Riverside County, where Quintero lives, now have these programs, according to the National Association of County and City Health Officials. Many were designed to shelter people experiencing homelessness but can be used to isolate others.
Raymond Niaura, interim chairman of the Department of Epidemiology at New York University, said these programs are used inconsistently and have been poorly promoted to the public.
“No one has done this before and a lot of what’s happening is that people are making it up as they go along,” said Niaura. “We’ve just never been in a circumstance like this.”
Quintero still worries about bringing the virus home to her family and fears being in the same room with her grandmother. Quintero returns from work every day now, puts her clothes in a separate hamper and diligently washes her hands before she interacts with anyone.
The bills have been another constant worry. Quintero called the hospital and her insurance company and complained that she should not have to pay since she was seeking a test on her doctor’s orders. Neither budged, and the bills labeled “payment reminders” soon became “final notices.” She reluctantly agreed to pay $100 a month toward her balance — $50 to the hospital and $50 to the doctors.
“None of them wanted to work with me,” Quintero said. “I just have to give the first payment on each bill so they wouldn’t send me to collections.”
Bill Of The Month Resources
The Takeaway: If you suspect you have COVID-19 and need to isolate to protect vulnerable members of your household, call your local public health department. Most counties have isolation and quarantine programs, but these resources are not well known. You may be placed in a hotel, recreational vehicle or other type of housing while you wait out the infection period. You do not need to have a positive COVID test to qualify for these programs and can use these programs while you await your test result. But this is an area in which public health officials repeatedly offer clear guidance — 14 days of isolation — which most people find impossible to follow.
At this point in the pandemic, tests are more widely available and federal law is very clearly on your side: You should not be charged any cost sharing for a coronavirus test.
Be wary, though, if your doctor directs you to the emergency room for a COVID test, because any additional care you get there could come at a high price. Ask if there are any other testing sites available.
If you do find yourself with a big bill related to suspected COVID, push beyond a telephone call with your insurance company and file a formal appeal. If you feel comfortable, ask your employer’s human resources staff to argue on your behalf. Then, call the help line for your state insurance commissioner and file a separate appeal. Press insurers — and big companies that offer self-insured plans — to follow the spirit of the law, even if the letter of the law seems to let them off the hook.
Bill of the Month is a crowdsourced investigation by Kaiser Health News and NPR that dissects and explains medical bills. Do you have an interesting medical bill you want to share with us? Tell us about it!
Foto: Haeidi de Marco.
Sarah Varney: svarney@kff.org, @SarahVarney4
Heidi de Marco: heidid@kff.org, @Heidi_deMarco
Photos by Heidi de Marco